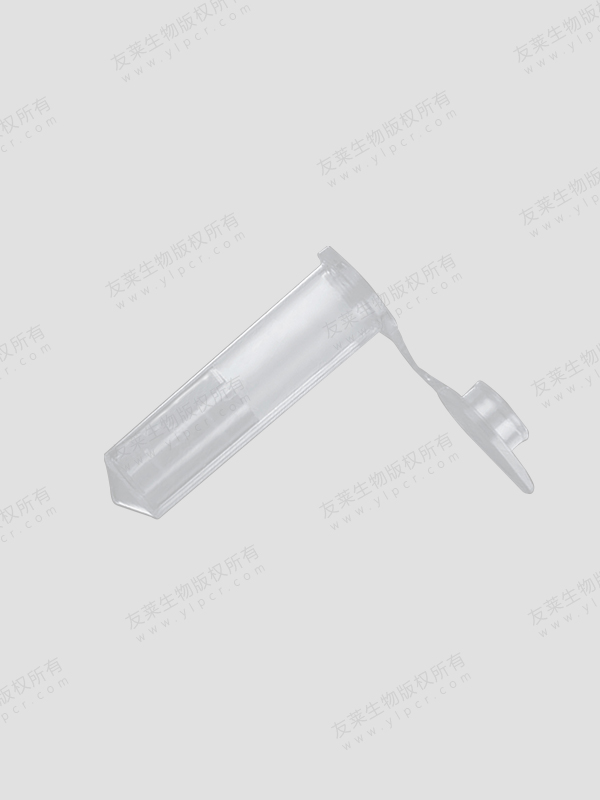
Cryovial tubes are a cornerstone in scientific research, particularly in fields such as molecular biology, biochemistry, and medical diagnostics. These specialized containers are designed for the storage and preservation of biological samples at ultra-low temperatures, often down to -196°C, which is the temperature of liquid nitrogen. The ability to safely store samples at such low temperatures is crucial for maintaining the integrity and viability of biological materials over extended periods.
Cryovial tubes, also known as cryogenic vials, are small, cylindrical containers made from materials that can withstand extreme cold. Typically, these tubes are constructed from high-quality polypropylene or polycarbonate, which are durable, chemically resistant, and have excellent low-temperature properties. They are designed to be leak-proof and often feature screw caps with silicone or rubber O-rings to ensure a tight seal, preventing contamination and evaporation.
Temperature Resistance: Cryovial tubes are engineered to remain stable at cryogenic temperatures, ensuring that the samples inside are not compromised. This makes them suitable for long-term storage in liquid nitrogen or ultra-low temperature freezers.
Sterility: To prevent contamination, cryovial tubes are often pre-sterilized using gamma radiation or ethylene oxide gas. This is critical for applications in microbiology and clinical research, where sterility is paramount.
Leak-Proof Design: The secure sealing mechanisms of cryovial tubes are designed to prevent leaks, which could lead to sample loss or contamination. This is especially important when storing hazardous or valuable samples.
Clear Labeling: Many cryovial tubes feature large, clear writing areas or barcodes for easy identification. This is essential for maintaining accurate records and ensuring that samples can be quickly and reliably identified.
Variety of Sizes: Cryovial tubes come in various sizes, typically ranging from 0.5 mL to 5 mL, to accommodate different volumes of samples.

 English
English русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体