PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Sealing Film is an essential component in molecular biology laboratories, crucial for ensuring the integrity and accuracy of PCR experiments. This thin, often adhesive film is designed to cover sample wells in PCR plates, preventing contamination and evaporation while allowing for optimal reaction conditions.
Material Composition
Typically made from materials such as polyethylene or polypropylene, PCR sealing films are engineered for thermal stability and chemical resistance. These materials provide excellent sealing properties, preventing the escape of volatile components during the PCR process. The choice of material directly impacts the film's performance, including its ability to withstand the high temperatures required during thermal cycling.
Sealing Performance
One of the primary functions of PCR sealing film is to create a reliable barrier against contamination from external sources. This is particularly important in PCR, where even minute amounts of contaminants can lead to false positives or negatively affect results. The sealing film ensures that the samples remain isolated, providing a sterile environment for the PCR reactions.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance
PCR processes often involve rapid temperature changes, requiring the sealing film to maintain its integrity under extreme conditions. High-quality PCR sealing films can endure these temperature fluctuations without compromising their sealing capabilities. Additionally, they exhibit resistance to various chemicals, including common reagents used in PCR, thus maintaining the reliability of the experiments.
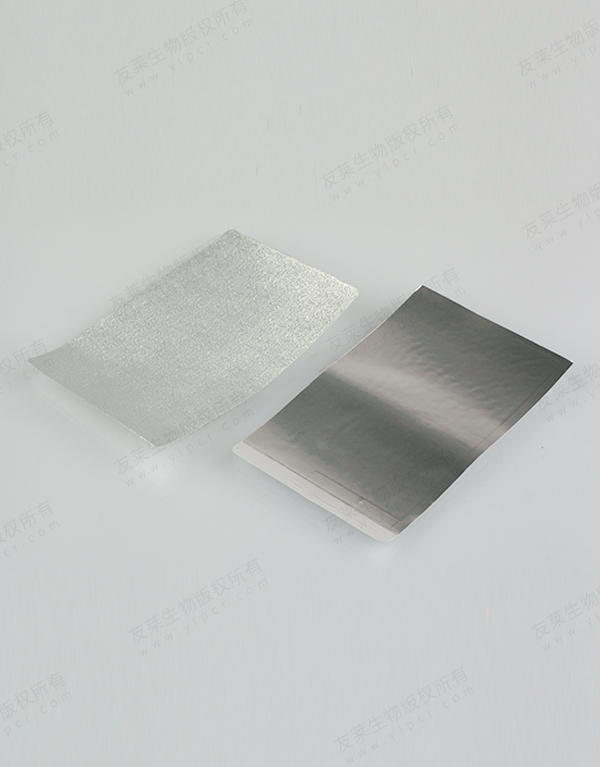

Breathability and Gas Exchange
While sealing films provide a robust barrier, they must also allow for adequate gas exchange. Some PCR sealing films are designed with micro-porous features that facilitate this exchange, preventing gas buildup that could affect the PCR reaction. This balance between sealing and breathability is crucial for achieving optimal amplification of DNA or RNA.
Application in Various Techniques
Beyond standard PCR, these films are versatile and can be utilized in other molecular techniques, such as quantitative PCR (qPCR) and reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). Their adaptability makes them a staple in laboratories focused on genetics, diagnostics, and research.
Market Trends and Innovations
The demand for PCR sealing films has surged, particularly with the rise of genetic testing and research initiatives. Manufacturers are continually innovating to enhance the properties of these films. Recent advancements include biodegradable options and films that reduce evaporation rates even further, catering to environmentally conscious laboratories.

 English
English русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体